The crew reported that when they made preparations for descent the Cairns Automatic Terminal Information Service (ATIS) nominated runway 15 for landing. The crew selected the appropriate approach and landing charts and programmed the flight management computer (FMC) for an arrival to runway 15.
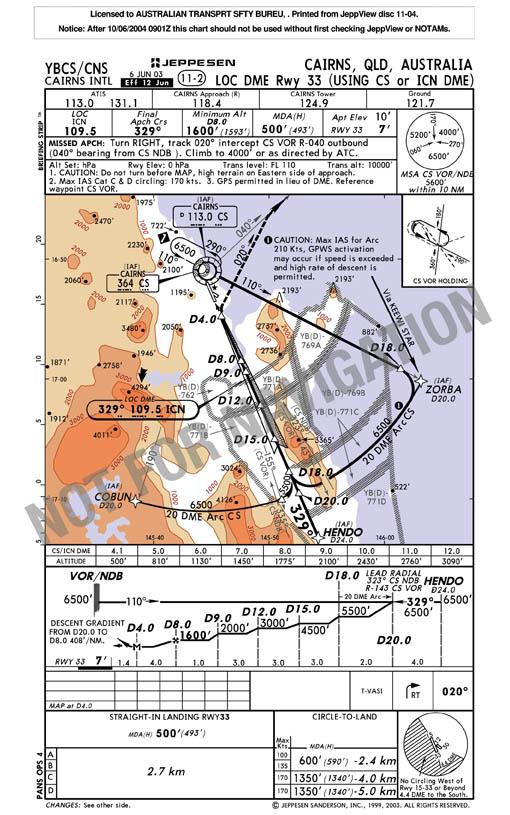
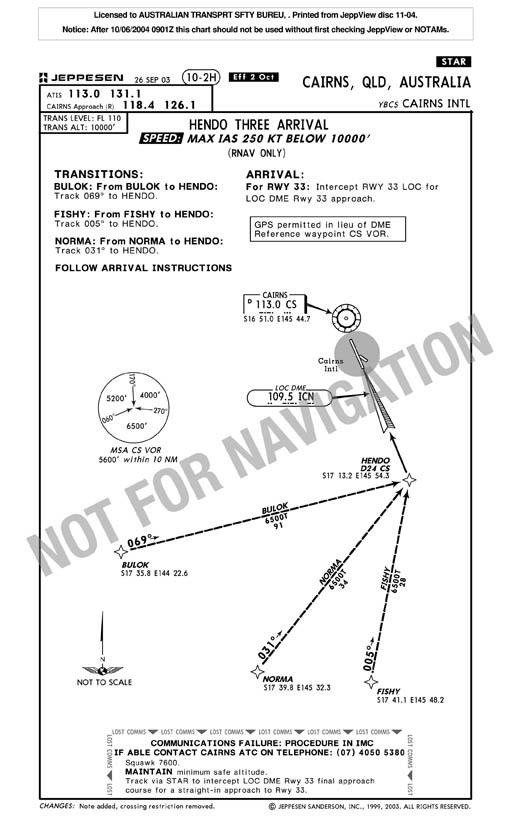
Three minutes before the crew commenced descent, the ATIS was changed to indicate that arriving aircraft from the south could expect to carry out the runway 33 Locator/Distance Measuring Equipment (LOC/DME) approach to runway 33. The crew was not aware of the change to the landing runway until the air traffic controller assigned the crew a HENDO-Three standard instrument arrival (STAR) which included a NORMA transition. In order to comply with the STAR, the 737 was required to proceed via waypoint NORMA and then track 031 degrees to waypoint1 HENDO, which, as the last waypoint of the STAR, also became the initial approach fix (IAF) for the runway 33 LOC/DME approach (Refer figure 1 & 2).
The crew selected the STAR and the runway 33 LOC/DME approach from the FMC navigation database and incorporated the required tracking and altitude requirements into the active FMC-LEGS page. During that interaction the crew did not select waypoint HENDO as the IAF when prompted by the FMC to do so and consequently critical 'Not below 6,500 ft' altitude constraints at the HENDO and 20 DME Cairns waypoints were omitted. The STAR and runway 33 LOC/DME approach became part of the FMC active flight plan and the FMC provided the crew with lateral and vertical navigation guidance.
While on descent, the crew was instructed by air traffic controller to reduce speed and fly a heading that would take the aircraft away from the published STAR track. The crew subsequently reported that this was done to ensure separation with preceding traffic. Once the required separation had been achieved, the crew was instructed to rejoin the localiser approach. They modified the route legs (RTE LEGS) page of the FMC by selecting track direct (TRK DCT) to HENDO. That action removed waypoints from the active route that were no longer required.
At 24 DME, the FMC calculated descent point, the aircraft left 6,500 ft. That occurred because the waypoints and their associated altitude constraints, which ensured that the aircraft would not descend below 6,500 ft until passing 20 DME had been omitted. The autopilot was engaged with vertical navigation (VNAV) mode active.
Analysis of information recovered from the flight data recorder showed that the 737 passed 20 DME Cairns at an altitude of 5,860 ft. The crew reported to air traffic control (ATC) that they were in cloud.
Figure 1: Cairns LOC DME Rwy 33
Reprinted with permission of Jeppesen Sanderson Inc.
Figure 2: Cairns - HENDO THREE ARRIVAL
Reprinted with permission of Jeppesen Sanderson Inc.
Cairns runway 33 LOC/DME approach
To ensure appropriate terrain clearance, flight crews conducting the Cairns runway 33 LOC/DME approach must maintain track within appropriate tolerances and not descend below the minimum altitude specified on the instrument approach chart until passing the next step-down point. Once the next step-down point has been passed, the aircraft is permitted to descend to the next lower minimum altitude. That allows crews to progressively descend, remaining safely clear of terrain as the aircraft approaches the airport for landing.
In order to accommodate aircraft arrivals from various directions, the Cairns runway 33 LOC/DME approach has a number of IAFs. Depending on the STAR issued by ATC, the crew should operate the aircraft to track via COBUN, HENDO, or ZORBA. The IAF forms an integral part of the runway 33 LOC/DME approach.
Flight Management Computer
The FMC system fitted to the 737 provided lateral and vertical flight path guidance as well as performance information to the crew. The FMC can also provide control and guidance information to the autopilot.
The 737 autopilot and flight director system has a number of descent modes. The crew reported that they conducted the Cairns runway 33 LOC/DME approach using VNAV2 path.
Before the crew could utilise the FMC to provide vertical navigation guidance, the FMC needed to compute a descent path, which conformed to the requirements of the instrument approach. Waypoints and associated altitude constraints required by the FMC to compute an accurate approach profile that corresponded to the LOC/DME approach path gradient had been inadvertently omitted by the crew.
The FMC database contained the Cairns runway 33 LOC/DME approach, which the crew selected. They were then prompted to select from one of three transitions; COBUN, HENDO, or ZORBA. During the occurrence flight, the FMC operated as designed.
Communication of safety information
The Operator's Operations Manual included detailed instructions to ensure that crews selected the HENDO transition when activating the runway 33 LOC/DME approach into the FMS.
The operator experienced similar events on three occasions during December 2003. In response to those occurrences the operator produced an article for its Safety Shorts Operational newsletter, which warned crews to follow published procedures when conducting a Cairns runway 33 LOC/DME approach.
The operator's manuals contained the following instruction:
The 737 Flight Crew Training Manual (FCTM)
Set all mandatory altitude restrictions and at or above constraints in the MCP altitude window. The next altitude may be set when the restriction has been assured, and further clearance has been received.
The Flight Crew Operations Manual (FCOM) (Part B) Volume B1 Approaching intercept heading, select flaps 5 and select LNAV or other appropriate roll mode. Approaching the FAF, select gear down and flap 15. Set the [altitude] minima in the MCP altitude window.
Crew communication during instrument approaches
The FCOM issued to crew members referred to the crewmembers as either the pilot flying (PF) or pilot not flying (PNF) and contained the following instruction regarding support calls:
Operations Manual (Part B) 2.11.3.9
On a non-ILS instrument approach, including DME Arrival, the PF shall brief the descent profile to be flown from the Final Approach Fix (FAF). After passing the FAF, the PNF shall call the profile (distance/altitude) at each published or briefed distance/altitude. The PF shall acknowledge the call and initiate any profile correction. The PNF shall then call the next profile distance/altitude.
Note: In the case of the Cairns 33 LOC/DME approach the FAF is at 8 DME.
The PNF was required to provide support calls (of distance/altitude) from the FAF. No calls were required to be made between the IAF, and the FAF. In the case of the Cairns runway 33 LOC/DME approach, the aircraft may be as low as 1,600 ft (the minimum altitude at 8 DME) before any calls were required to be made. The aircraft was between the IAF and the FAF when it descended below 6,500 ft.
- Predetermined and accurately known geographical position forming start or end of route segment.
- Vertical navigation mode