Update: 10 December 2015
The ATSB has issued an update to clarify its recently released report MH370 - Definition of Underwater Search Area.
The update establishes that the ‘power loss’ mentioned on page 9 occurring between 17:07:48 and 18:03:41 was referring to the Satellite Data Unit (SDU) only. The SDU did not respond to an automatic interrogation from the Ground Earth System (GES) at 18:03:41 UTC, although it resumed working at 18:25:27.
Report released: 3 December 2015
This report provides an update to the MH370 search area definition, described in previous ATSB reports. For background information, please see the ATSB publications MH370 - Definition of underwater search areas, 18 August 2014 and Flight Path Analysis Update, 8 October 2014 under the tabs on this web page.
Analysis of available data has been ongoing since the search for MH370 commenced. Initial results assisted the search and rescue mission, and later refinements have formed the basis for the underwater search areas.
The Australian Defence Science and Technology (DST) Group conducted a comprehensive analysis of the available data. The analysis used models of the Inmarsat satellite communications (SATCOM) data and a model of aircraft dynamics. Recorded meteorological data (wind and air temperature) were also modelled in the analysis. The SATCOM model was calibrated using SATCOM data and flight data from B777 flights including previous flights of the accident aircraft.
Validation experiments were conducted to ensure that predictions aligned with actual flight data. The output of the DST Group analysis was a probability density function (PDF) defining the probable location of the aircraft’s crossing of the 6th arc. These results were then extrapolated to the 7th arc. The analysis indicated that the majority of solutions only contained one significant turn after the last recorded radar data. DST Group have written a book called Bayesian methods in the search for MH370 detailing the entire analysis.
Performance analysis by Boeing produced a series of achievable ranges, with time intervals, for different cruise altitudes. It was noted that maintaining a constant altitude of FL350 or higher gave range values that closely matched the region on the arc corresponding to the DST Group analysis results. The DST Group and Boeing results were obtained independently and it is significant that they were in general agreement.
In contrast to the series of data points that were recorded from the SATCOM system, only the following indirect information was available to assist the ATSB in determining the end-of-flight scenario and therefore determine a search area width:
- probable aircraft systems status
- simulator results
- review of previous accidents
- glide distance.
The original ATSB underwater search area definition report published in August 2014 identified a width of 20 NM behind the arc and 30 NM forward of the arc as the priority search area width. This primary priority width has been adjusted to make it symmetrical about the arc (20 NM on both sides). The ATSB has also defined and prioritised additional search area widths.
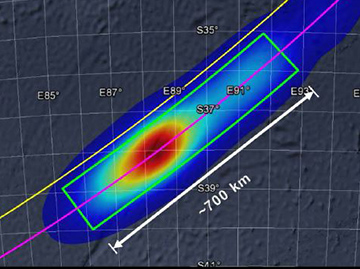
The probability distribution of the location of the aircraft is shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1: Probability distribution of the location of MH370

Ongoing work:
Any further evidence that becomes available, and may be relevant to refining the search area,will be considered.
- MH370 - Definition of Underwater Search Area
- Bayesian Methods in the Search for MH370 by Defence Science and Technology Group, Australia. This analysis has informed the ATSB’s latest report, MH370 – Definition of Underwater Search Area.
- Read more about MH370


